-
Adverse ReactionsAdverse Reactions in the Study Safety Population (reported in ≥20% of patients in the IsaKd arm)1
IsaKd (n=177) Kd (n=122) All Grades ≥Grade 3 All Grades ≥Grade 3 Most Common Infections (%) Upper respiratory tract infection* 66.7 9.0 57.0 7.0 Pneumonia† 36.2 22.0 30.0 18.0 Bronchitis‡ 23.7 2.3 13.0 0.8 Most Common Adverse Reactions in Other Organ Systems (%) Infusion reactions§ 45.8 0.6 3.3 0 Fatigue¶ 41.8 5.0 32.0 3.3 Hypertension∆ 37.3 21.0 32.0 20.0 Diarrhea 36.2 2.8 29.0 2.5 Dyspnea# 28.8 5.0 24.0 0.8 Cough« 23.0 0 15.0 0 -
Serious Adverse ReactionsMost Common Serious Adverse Reactions in the Study Safety Population Occurring with Incidences >5%1
IsaKd (n=177) Kd (n=122) Pneumonia 24.9% 18.0% Upper respiratory tract infection 9.0% 8.2% -
Treatment-Emergent Laboratory AbnormalitiesTreatment-Emergent Laboratory Abnormalities in the Study Safety Population1
IsaKd (n=177) Kd (n=122) All Grades ≥Grade 3 All Grades ≥Grade 3 Adverse Reaction (%) Anaemia 99.4 22.0 99.2 19.7 Lymphopenia 94.4 68.9 95.1 57.3 Thrombocytopenia 94.4 29.9 87.7 23.8 Neutropenia 54.8 19.2 43.4 7.4 The denominator used for the percentage calculation is the number of patients with at least 1 evaluation of the laboratory test during the considered observation period.
CHARACTERISTICS
* Upper respiratory tract infection includes acute sinusitis, chronic sinusitis, H1N1 influenza, H3N2 influenza, influenza, laryngitis viral, nasal herpes, nasopharyngitis, pharyngitis, pharyngotonsillitis, respiratory syncytial virus infection, rhinitis, sinusitis, sinusitis bacterial, tonsillitis, tracheitis, upper respiratory tract infection, viral rhinitis, respiratory tract infection, respiratory tract infection viral, influenza like illness, parainfluenzae virus infection, respiratory tract infection bacterial, and viral upper respiratory tract infection.
† Pneumonia includes atypical pneumonia, lower respiratory tract infection, lower respiratory tract infection viral, pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, pneumonia, pneumonia influenzal, pneumonia legionella, pneumonia pneumococcal, pneumonia respiratory syncytial viral, pneumonia streptococcal, pneumonia viral, pulmonary sepsis, and pulmonary tuberculosis.
‡ Bronchitis includes bronchitis, bronchitis viral, respiratory syncytial virus bronchitis, bronchitis chronic, and tracheobronchitis.
§ Infusion-related reaction includes infusion-related reaction, cytokine release syndrome, and hypersensitivity.
¶ Fatigue includes fatigue and asthenia.
∆ Hypertension includes hypertension, blood pressure increased, and hypertensive crisis.
# Dyspnea includes dyspnea and dyspnea exertional.
« Cough includes cough, productive cough, and allergic cough.
IsaKd, isatuximab + KYPROLIS + dexamethasone; Kd, KYPROLIS + dexamethasone.
| Characteristics | IsaKd (n=179) | Kd (n=123) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | ||
| Median (years) | 65 | 63 |
| Range (years) | 55–70 | 57–70 |
| Distribution [number of patients (%)] | ||
| <65 | 88 (49) | 66 (54) |
| 65–74 years | 74 (41) | 47 (38) |
| ≥75 years | 17 (9) | 10 (8) |
| ECOG Performance Status [number of patients (%)] | ||
| 0 | 95 (53) | 73 (59) |
| 1 | 73 (40) | 45 (37) |
| 2 | 10 (6) | 5 (4) |
| Cytogenic Risk at Study Entry [number of patients (%)] | ||
| High risk* | 42 (23) | 31 (25) |
| Standard risk | 114 (64) | 78 (63) |
| Unknown | 23 (13) | 14 (11) |
| Prior Therapies | IsaKd (n=179) | Kd (n=123) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 prior line of therapy | 79 (44) | 55 (45) |
| 2 prior lines of therapy | 64 (36) | 36 (29) |
| 3 prior lines of therapy | 33 (18) | 30 (24) |
| Autologous transplant | 116 (65) | 69 (56) |
| Previous proteasome inhibitor | 166 (93) | 105 (85) |
| Previous immunomodulators | 136 (76) | 100 (81) |
| Previous lenalidomide | 72 (40) | 59 (48) |
| Prior daratumumab | 1 (1) | 0 (0) |
- Patients with relapsed and/or refractory multiple myeloma
- Patients must have received 1 to 3 prior lines of therapy
- Patients were excluded if they had primary refractory disease or were refractory to previous anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody treatment
* High-risk cytogenetic status defined as the presence of del(17p) or translocation t(4;14) or translocation t(14;16).
ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; ITT, intent to treat; IsaKd, isatuximab + KYPROLIS + dexamethasone; Kd, KYPROLIS + dexamethasone.
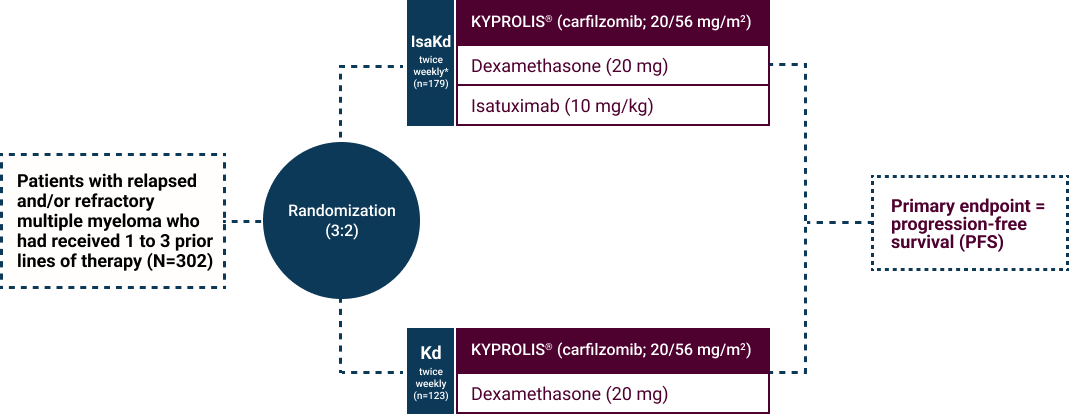
* Cycles were repeated until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Isatuximab was administered weekly in the first cycle and every two weeks in the following cycles.
PFS was determined by an Independent Review Committee.1
IsaKd, isatuximab + KYPROLIS + dexamethasone; Kd, KYPROLIS + dexamethasone; PFS, progression-free survival.


